Implications for CEOs
For CEOs, understanding and leveraging AI, especially Gen AI, is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and driving business innovation. The adoption of Gen AI presents unique challenges and opportunities, from managing emerging risks and ethical considerations to rethinking talent strategy. As AI becomes increasingly integral to business strategy, CEOs must navigate these complexities to ensure their organizations not only adapt to these technological advancements but also lead the way in this new digital era.
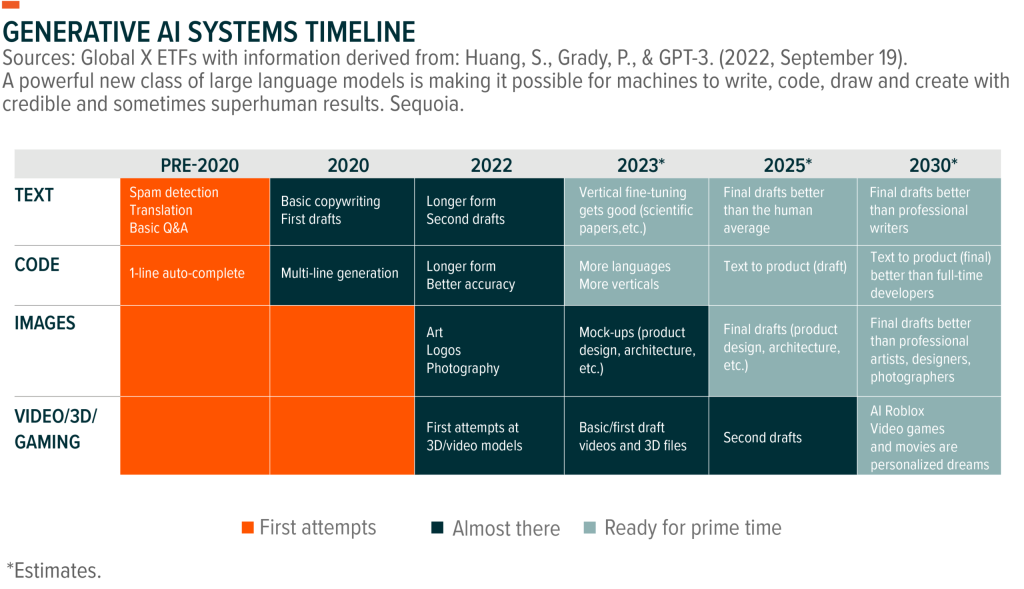
We are at the dawn of the “augmented workforce” era — a transformative period where humans and machines collaborate, driving remarkable productivity and creating new value for businesses. The World Economic Forum forecasts a seismic shift by 2025, with technology remapping the employment landscape, phasing out 85 million jobs but simultaneously introducing 97 million novel roles. This dynamic is the essence of innovation, marking a paradigm shift in the labor market.
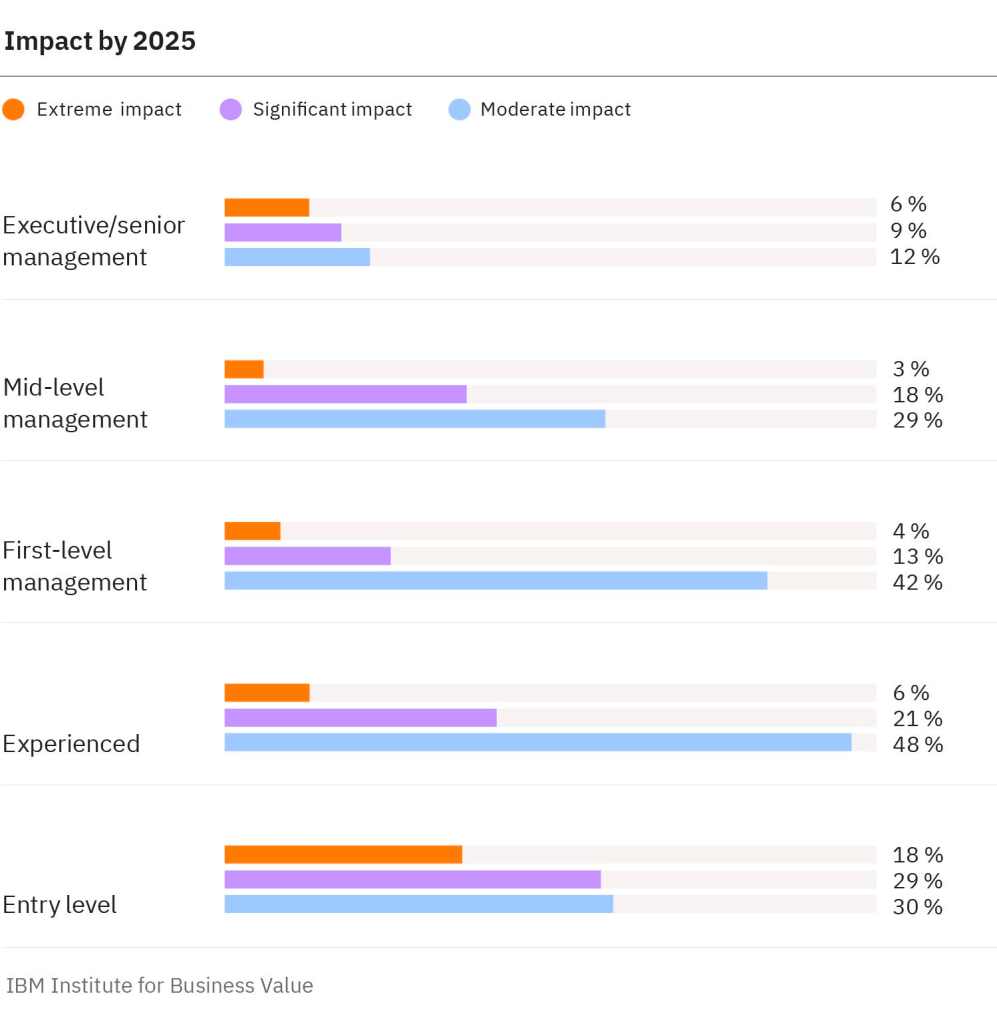
However, this transition brings a widening skills gap, a concern echoed by the World Economic Forum. They project that nearly half (44%) of the current skill sets will be obsolete or altered significantly within the next five years, marking an increase from previous predictions. The advent of generative AI stands to amplify this trend, as suggested by a study from the IBM Institute for Business Value. This survey highlights an executive consensus: four out of five leaders believe generative AI will revolutionize job roles and requisite skills.
The ripples of this shift will touch employees at every level, but those in entry-level positions are poised to experience the most pronounced changes. As businesses and workers navigate this new landscape, the ability to adapt to and embrace these technologies will become a pivotal aspect of workforce development and competitive advantage.
We are at the dawn of the “augmented workforce” era — a transformative period where humans and machines collaborate, driving remarkable productivity and creating new value for businesses. The World Economic Forum forecasts a seismic shift by 2025, with technology remapping the employment landscape, phasing out 85 million jobs but simultaneously introducing 97 million novel roles. This dynamic is the essence of innovation, marking a paradigm shift in the labor market.
However, this transition brings a widening skills gap, a concern echoed by the World Economic Forum. They project that nearly half (44%) of the current skill sets will be obsolete or altered significantly within the next five years, marking an increase from previous predictions. The advent of generative AI stands to amplify this trend, as suggested by a study from the IBM Institute for Business Value. This survey highlights an executive consensus: four out of five leaders believe generative AI will revolutionize job roles and requisite skills.
In the upcoming sections, we’ll delve deeper into these topics, providing insights and strategies for CEOs to harness AI’s potential effectively. This exploration will cover the multifaceted impact of AI on business, offering a roadmap for leaders to navigate this rapidly evolving landscape.
AI’s Strategic Importance in Business
The evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) from a purely technical endeavor to a core strategic business focus marks a significant shift in the corporate world. This section explores how AI, particularly generative AI (Gen AI), is influencing boardroom agendas, driving investment trends, and reshaping business strategies.
From Technical Novelty to Strategic Imperative
AI’s journey from the labs of data scientists to the strategic plans of boardrooms reflects its growing importance in driving business innovation and competitive advantage. Initially viewed as a tool for automating routine tasks and analyzing large datasets, AI is now recognized for its broader strategic value. It’s not just about efficiency; it’s about creating new business models, redefining customer experiences, and opening up untapped markets. This strategic pivot necessitates a deeper understanding and integration of AI at the highest levels of decision-making.
Gen AI in the Boardroom: More Than Just Buzz
The surge in interest and adoption of Gen AI is not just a passing trend. It’s a reflection of its potential to revolutionize how businesses operate. Gen AI tools, with their ability to generate new content and ideas, are now a topic of discussion in board meetings, influencing decisions on product development, marketing strategies, and customer engagement. The statistics are telling: a significant percentage of organizations report that Gen AI is not only used in various business functions but is also a subject of strategic discussions at the board level. This shift underscores the need for CEOs and board members to be well-versed in the capabilities and potential applications of Gen AI to guide their organizations effectively.
Investment Trends: Betting Big on AI
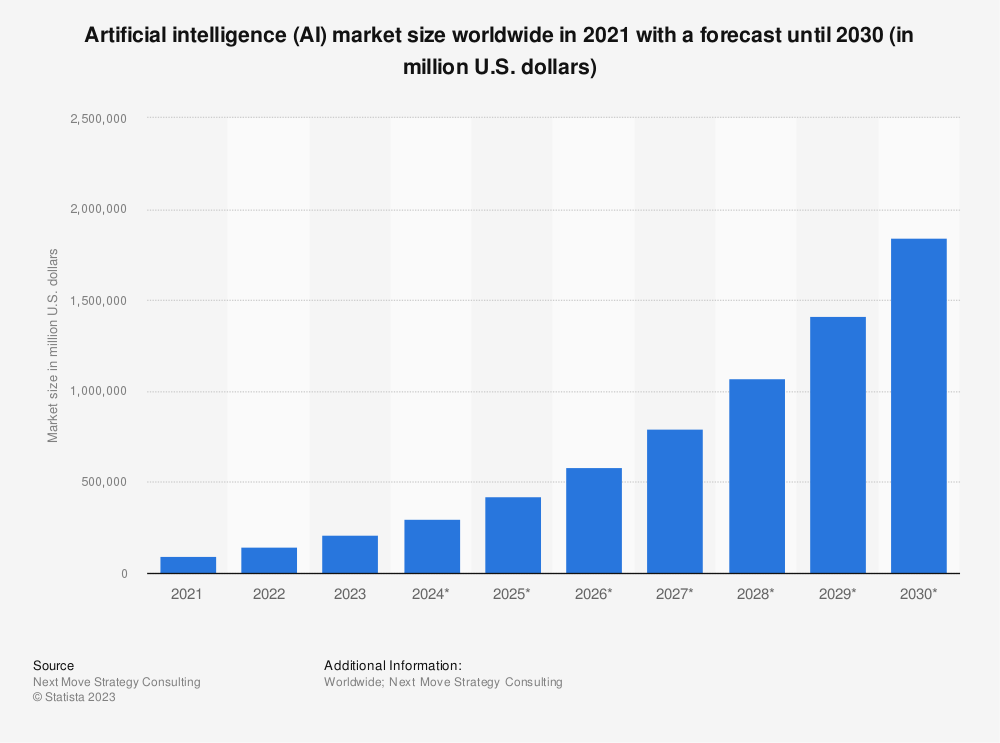
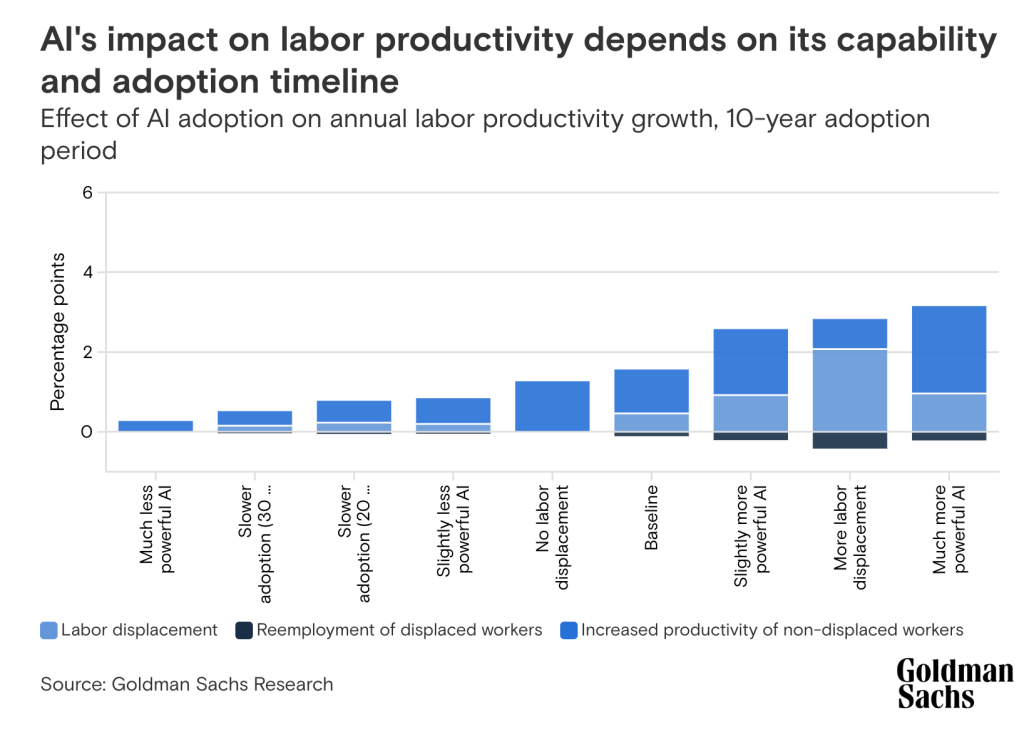
The advancements in Gen AI are catalyzing new investment trends in the AI space. Companies increasingly recognize the value of investing in AI, not just as a cost of doing business but as a strategic imperative to drive growth and innovation. The influx of investments is not limited to tech giants or specific sectors; it’s widespread across industries. This trend is fueled by the recognition that AI can unlock new value streams, enhance operational efficiencies, and create differentiated products and services. As a result, we’re seeing a significant uptick in the allocation of budgets toward AI initiatives, with a focus on Gen AI technologies.

Strategic Implications for Business Leaders
For CEOs and business leaders, these developments in AI signal a need for a strategic re-evaluation. It’s essential to consider how AI can be integrated into the broader business strategy beyond technical implementation. This involves understanding the potential of AI to drive business value, rethinking talent acquisition strategies to include AI expertise, and staying ahead of the curve in terms of regulatory and ethical considerations. As AI continues to evolve, the ability to adapt and leverage these technologies will be a crucial differentiator in the competitive business landscape.
AI’s Impact on Industry and Competition
The advent of generative AI (Gen AI) is not just transforming business operations; it’s reshaping the very fabric of industry competition. This section delves into the predicted changes in competitive dynamics due to Gen AI, its varied impacts across different industries, and real-world examples of its transformative power.
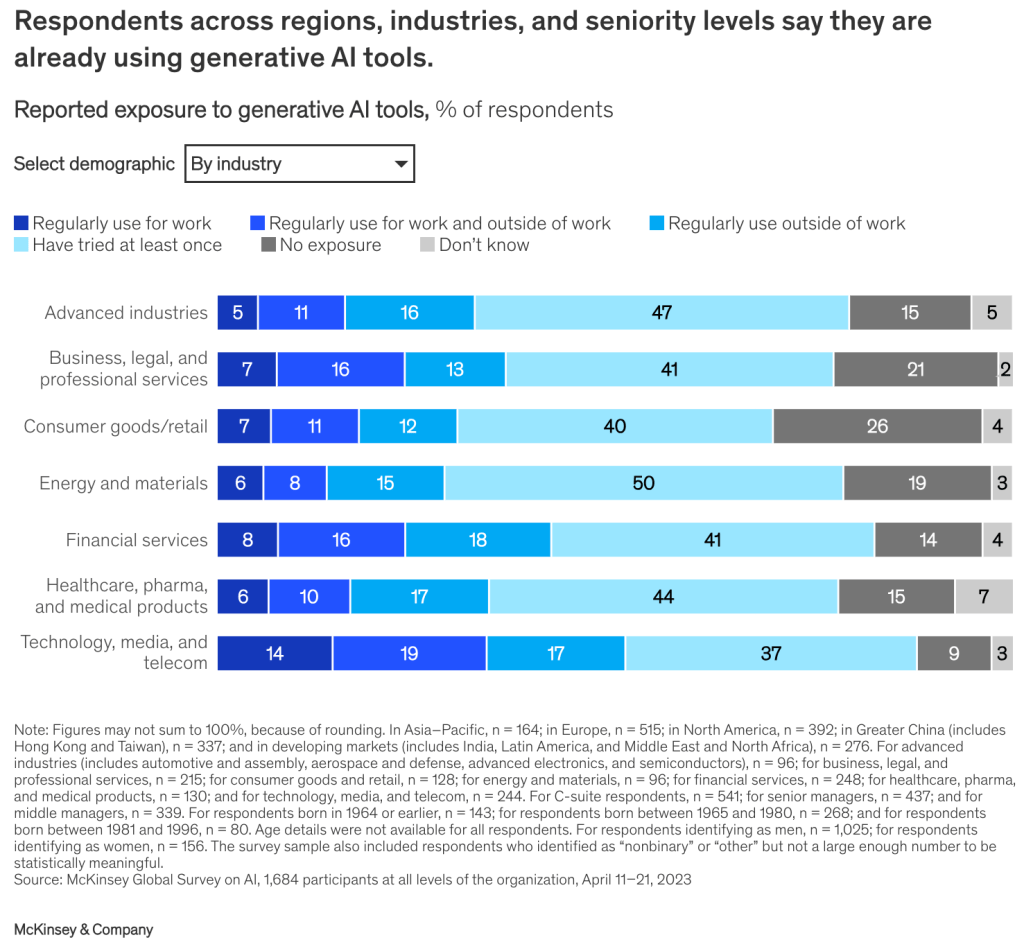
Changing the Competitive Landscape with Gen AI
Gen AI is poised to redefine the benchmarks of innovation, efficiency, and customer engagement across industries. Its ability to generate novel content and solutions is shifting the competitive advantage from traditional factors like cost and speed to innovation and personalization. Companies leveraging Gen AI are finding new ways to outpace competitors by creating more innovative products, offering highly personalized services, and enhancing customer experiences. This shift is expected to intensify competition, pushing companies to innovate and adapt to stay relevant continuously.
Diverse Impacts Across Industries
The impact of Gen AI varies significantly across different sectors. In creative industries like marketing and design, Gen AI is revolutionizing content creation, enabling personalized advertising campaigns and innovative design solutions at unprecedented scales. In sectors like finance and healthcare, Gen AI is being used to analyze vast datasets for insights into customer behavior, risk assessment, and predictive diagnostics respectively.
In manufacturing, Gen AI aids in optimizing production processes and predictive maintenance, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime. The technology sector itself is seeing a surge in new product developments and service offerings, driven by Gen AI’s capabilities in software development and problem-solving.
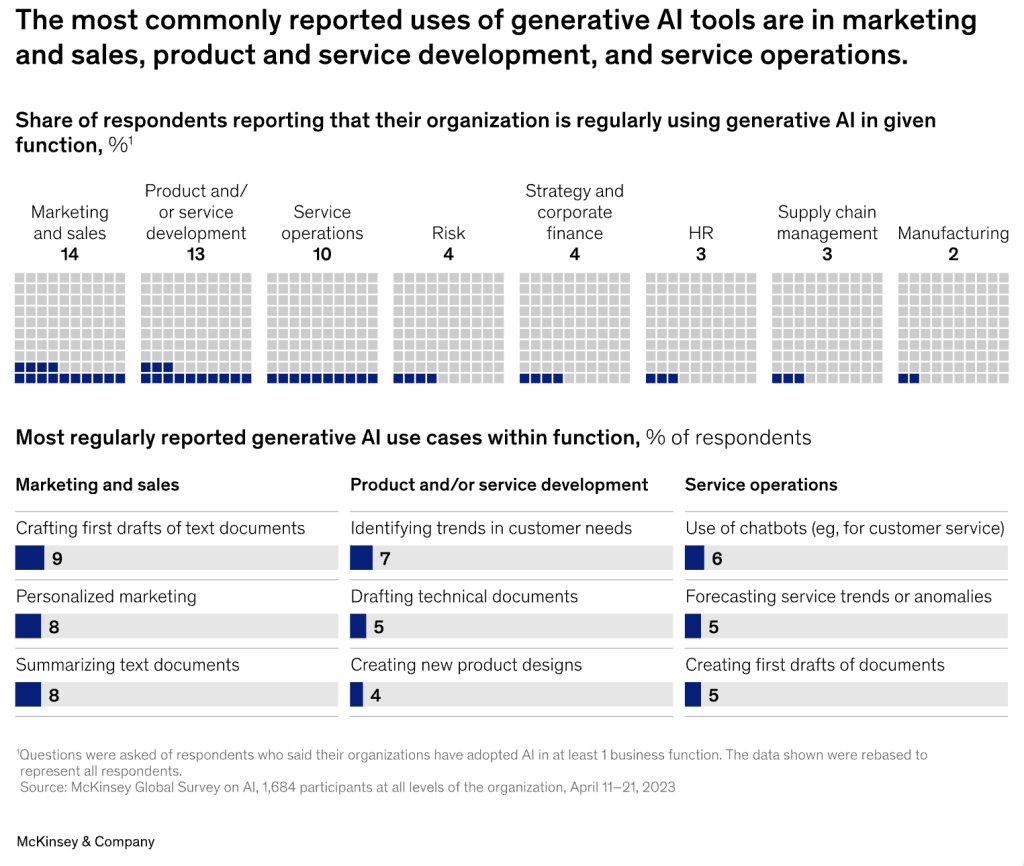
Real-World Examples of Gen AI at Work
- Marketing and Advertising: Companies use Gen AI to create dynamic and personalized advertising content that resonates more effectively with diverse consumer segments, leading to higher engagement rates and ROI.
- Healthcare: Gen AI is enabling breakthroughs in personalized medicine and diagnostics. For instance, AI-driven analysis of medical images and patient data is helping in early disease detection and tailored treatment plans.
- Finance: In the finance sector, Gen AI is being employed for more accurate and nuanced risk assessments, fraud detection, and personalized financial advice, transforming customer service and operational efficiency.
- Retail: Retail giants are leveraging Gen AI for inventory management, personalized shopping experiences, and optimizing supply chains, significantly enhancing customer satisfaction and operational agility.
- Manufacturing: In manufacturing, Gen AI is instrumental in streamlining production lines, predictive maintenance, and enhancing product design, leading to cost savings and improved product quality.
Managing Risks and Challenges in Gen AI
While generative AI (Gen AI) presents vast opportunities for innovation and growth, it also introduces a spectrum of risks and challenges. This section outlines the key risks associated with Gen AI, including inaccuracy, cybersecurity, and regulatory compliance, and discusses strategies for mitigating these risks, along with best practices from AI high performers.
Key Risks of Gen AI
- Inaccuracy: One of the primary concerns with Gen AI is the potential for generating inaccurate or biased outputs. Given that Gen AI models learn from vast datasets, there’s a risk of perpetuating existing biases or inaccuracies in the training data.
- Cybersecurity: As with any digital technology, Gen AI systems are susceptible to cybersecurity threats. Malicious actors could manipulate AI algorithms or access sensitive data, leading to significant security breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance: The rapidly evolving nature of AI technologies, including Gen AI, poses challenges in regulatory compliance. The lack of clear legal frameworks around AI-generated content and decision-making processes makes it difficult for organizations to ensure they’re not inadvertently violating laws or ethical norms.
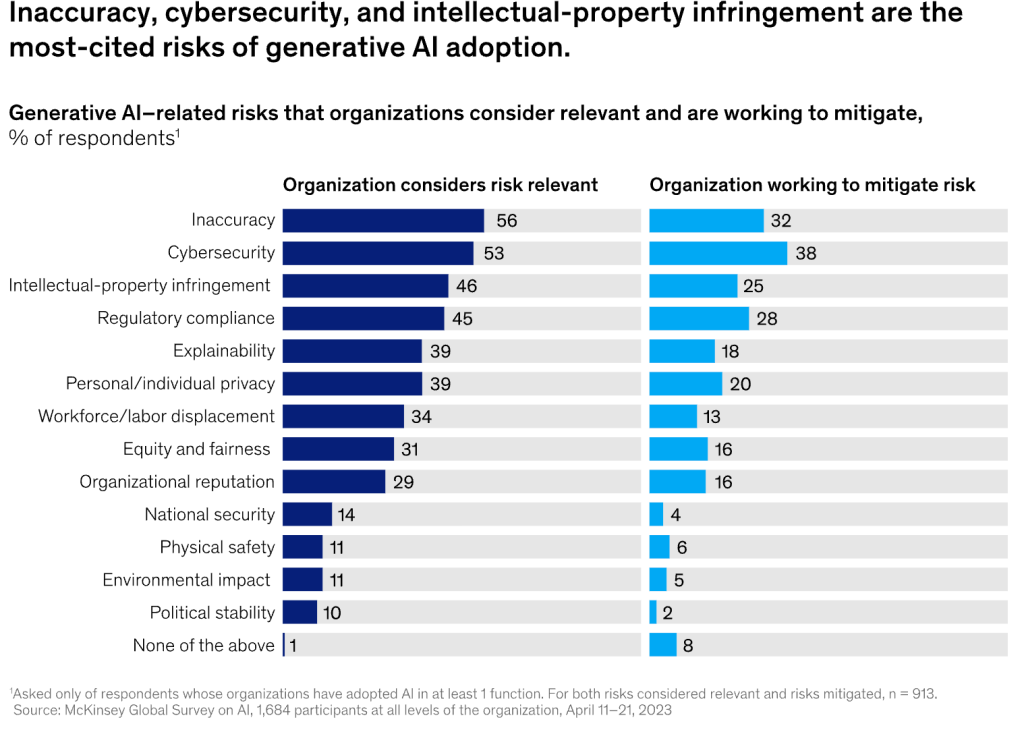
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
- Ensuring Data Integrity: To combat inaccuracy and bias, it’s crucial to ensure the integrity and diversity of the data used in training Gen AI models. Regular audits and updates of the data can help in identifying and mitigating biases.
- Robust Cybersecurity Measures: Implementing state-of-the-art cybersecurity protocols is essential. This includes regular security audits, using advanced encryption methods, and employing AI itself to detect and respond to security threats.
- Staying Abreast of Regulatory Changes: Organizations must actively monitor and adapt to the evolving legal landscape surrounding AI. This involves not only compliance with current regulations but also anticipating future legal trends and preparing accordingly. One such change is Biden’s Executive Order on AI.
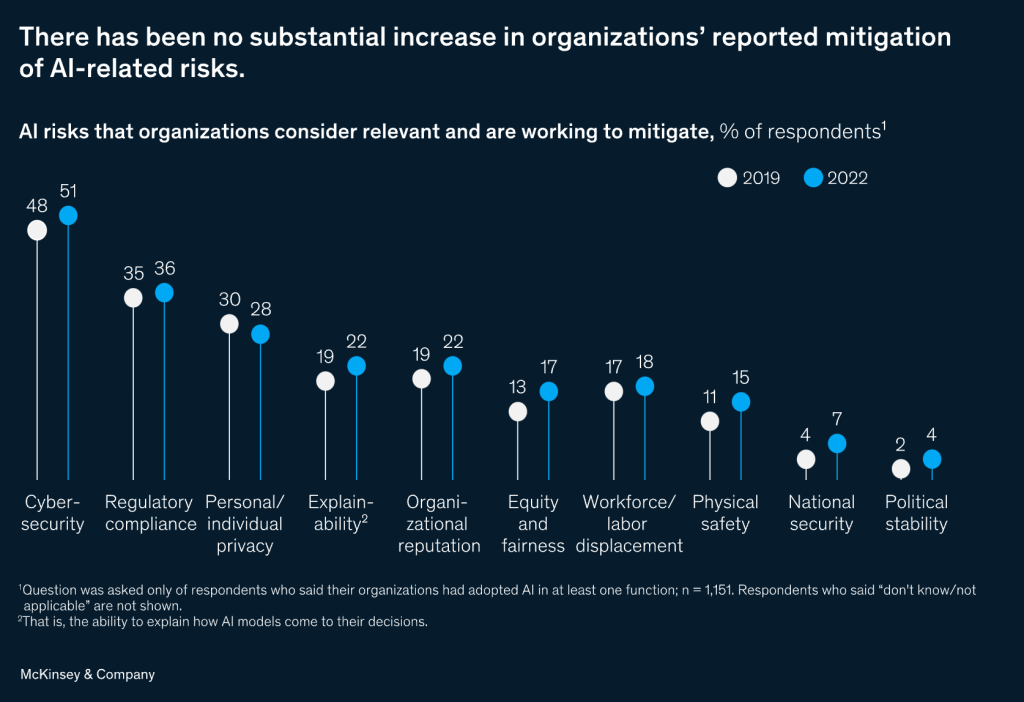
Best Practices from AI High Performers
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: High-performing organizations in AI don’t just implement solutions; they foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation. This involves regular training programs for staff, staying updated with the latest AI advancements, and being agile in adapting AI strategies.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: Leading companies establish ethical AI frameworks to guide their use of AI technologies. These frameworks typically include principles like transparency, fairness, accountability, and respect for user privacy.
- Collaboration and Openness: Successful AI adopters often emphasize collaboration – both internally across departments and externally with other organizations, regulatory bodies, and AI communities. This openness fosters innovation, ensures a broader understanding of AI implications, and helps share best practices.
Talent and Workforce Transformation in the Age of AI
The integration of AI and generative AI (Gen AI) into business processes is fundamentally altering the landscape of work, talent needs, and workforce strategies. This transformation is characterized by the emergence of new roles, the evolution of existing job functions, and the need for strategic reskilling and workforce optimization.
The average half-life of skills is now less than five years, and in some tech fields it’s as low as two and a half years. For millions of workers, upskilling alone won’t be enough.
Harvard Business Reviews: Reskilling in the Age of AI
Five new paradigms for leaders—and employees by Jorge Tamayo, Leila Doumi, Sagar Goel, Orsolya Kovács-Ondrejkovic, and Raffaella Sadun
Furthermore, as we move toward greater digitization, work processes are becoming more automated, and AI is replacing low-skilled jobs. This is driving increased interest in reskilling and upskilling among employees to ensure their career paths are secure. Coursera is well-positioned to benefit from this trend as it offers various courses and programs to help individuals acquire new skills and advance their careers.
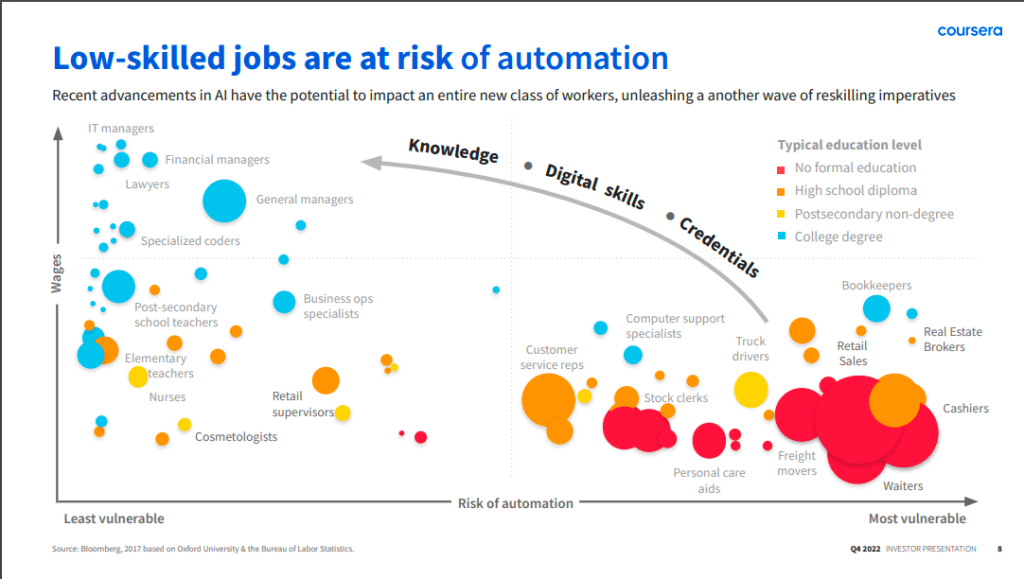
Shifts in AI-Related Talent Needs and Roles
- Emerging Roles: The rise of AI has led to the creation of specialized roles such as AI specialists, data scientists, machine learning engineers, and AI ethics officers. These roles are crucial for developing, managing, and ensuring the ethical use of AI technologies.
- Evolving Skill Sets: Alongside new roles, traditional jobs are also evolving to incorporate AI management, interpretation of AI outputs, and strategic integration of AI insights. This shift demands a workforce that is not only technically proficient but also adept in ethical and strategic decision-making related to AI.
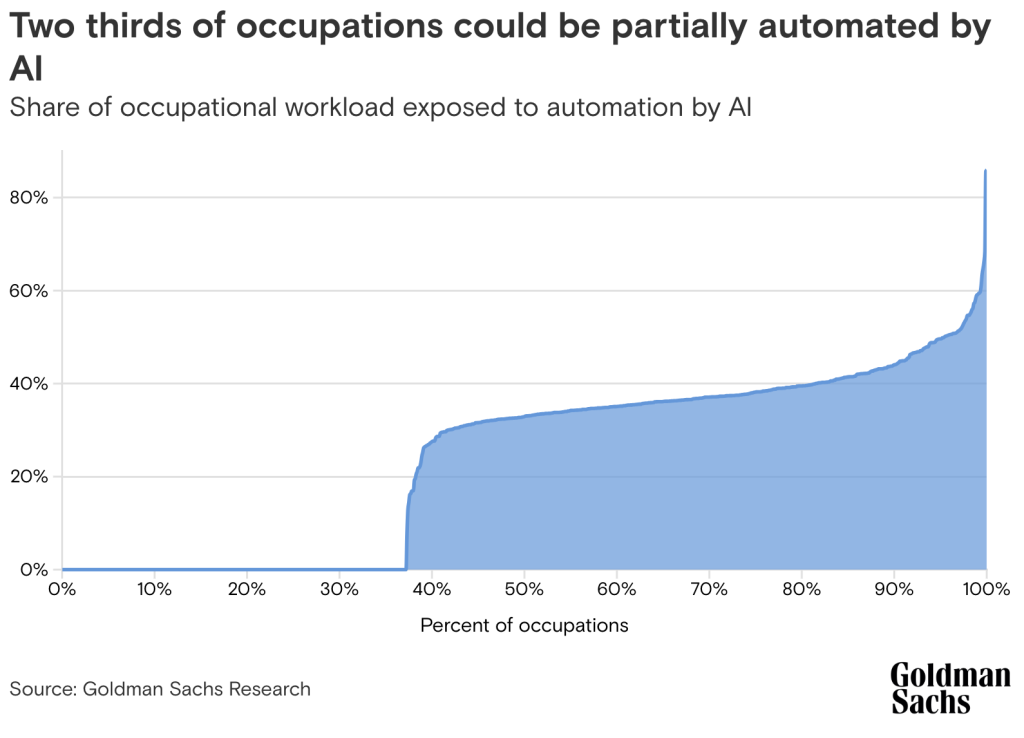
Impact of AI and Gen AI on Workforce Size and Skill Requirements
- Workforce Resizing: AI’s capability to automate tasks can lead to a reduction in certain types of jobs while simultaneously creating new opportunities requiring advanced skill sets. This duality highlights the dynamic nature of AI’s impact on workforce size and composition.
- Changing Skill Requirements: The demand for technical skills in AI, data analysis, and cybersecurity is rising. Simultaneously, there’s an increased need for soft skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, and ethical decision-making in AI contexts.
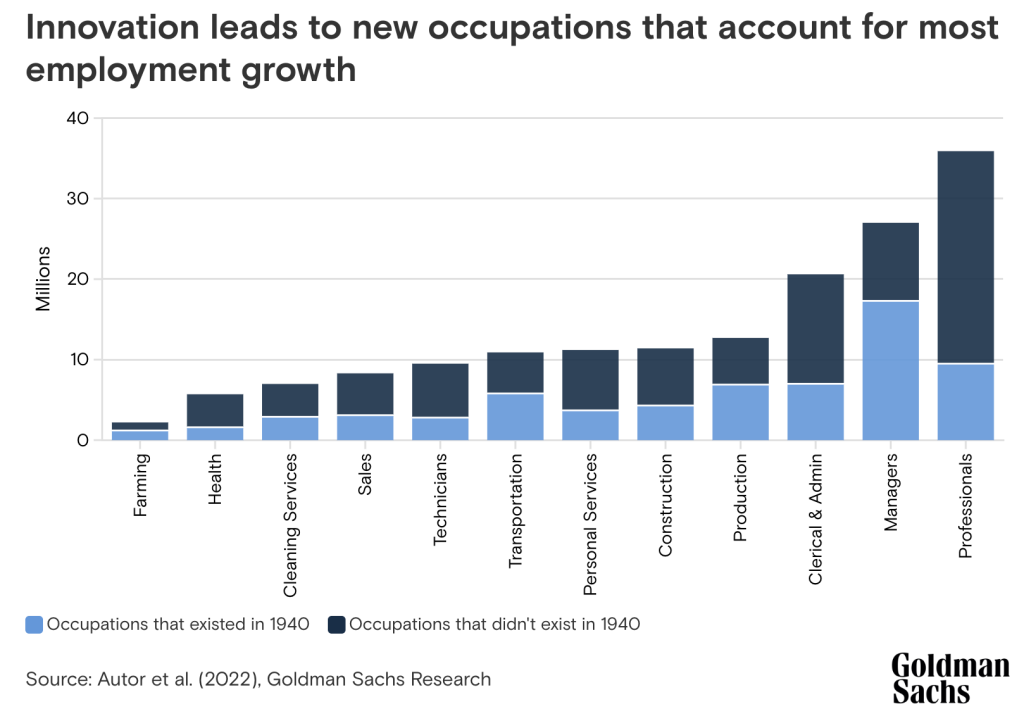
Strategies for Reskilling and Workforce Optimization
- Reskilling Initiatives: Proactive reskilling and upskilling of the workforce are essential to meet the evolving demands of an AI-driven business environment. This includes training in AI and data literacy, as well as specialized skills for emerging AI-related roles.
- Creating a Learning Culture: Cultivating a culture of continuous learning and adaptability is key to navigating the AI transformation. Encouraging ongoing education and professional development helps employees stay current with AI advancements.
- Strategic Hiring: To complement reskilling efforts, hiring new talent with specialized AI skills is crucial. This approach helps fill skill gaps, particularly in roles that focus on the broader social, ethical, and business implications of AI.
- Leveraging AI in HR: AI technologies can also optimize HR functions, from recruitment to performance analysis, aiding in more effective talent management and workforce optimization.
The transformation of talent and workforce in the age of AI and Gen AI presents challenges and opportunities. By understanding these shifts in talent needs, the impact on workforce dynamics, and implementing effective reskilling and workforce optimization strategies, businesses can successfully navigate these changes, ensuring a skilled, adaptable, and ethically aware workforce.
AI Adoption and Organizational Readiness
Adopting AI across various industries has been a pivotal point in organizational transformation. This section explores the current state of AI adoption, the challenges organizations face in capturing value from AI, and insights into how high-performing companies integrate AI more effectively.
Current State of AI Adoption Across Industries
- Varied Adoption Rates: AI adoption varies significantly across different industries. Sectors like technology, finance, and healthcare are leading in AI integration, using AI for everything from customer service automation to advanced diagnostics and risk analysis. Conversely, industries like manufacturing and logistics are adopting AI at a slower pace, focusing primarily on process automation and supply chain optimization.
- Depth of Integration: The depth of AI integration also varies. While some companies are using AI for specific tasks such as data analysis or customer service, others are embedding AI into their core business strategies, reshaping their entire business models around AI capabilities.
According to a survey by the Stanford HAI, 50% of organizations report using AI tools for at least one function within their operations. But as we look deeper, the power of AI as a customizable and multi-faceted tool becomes apparent:
| HR | Production | Marketing | Product | Risk | Service Ops | Corporate Finance | Supply Chain | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Industries | 11% | 8% | 5% | 10% | 19% | 19% | 21% | 9% |
| Professional Services | 11% | 10% | 9% | 8% | 16% | 20% | 19% | 12% |
| Retail | 14% | 4% | 3% | 4% | 15% | 31% | 29% | 11% |
| Financial Services | 1% | 8% | 7% | 31% | 17% | 24% | 23% | 2% |
| Healthcare | 15% | 7% | 2% | 4% | 22% | 12% | 8% | 8% |
| High Tech | 6% | 6% | 4% | 7% | 38% | 21% | 25% | 8% |
Generative AI programs such as DALL-E, Bard, and ChatGPT have also been adopted by significant number of people. In particular, OpenAI’s ChatGPT boasts 100 million users and over a billion monthly hits.
Challenges in Capturing Value from AI
- Data Quality and Accessibility: One of the biggest challenges in leveraging AI is the quality and accessibility of data. AI systems require large volumes of high-quality, relevant data to function effectively, which can be a significant hurdle for many organizations.
- Skill Gaps: The lack of AI expertise and understanding within organizations can hinder effective implementation. This includes not only technical skills but also the ability to integrate AI insights into strategic decision-making.
- Cultural Resistance: Organizational culture and resistance to change can also be significant barriers. Sometimes, there’s a lack of trust in AI-driven decisions or a fear of job displacement, leading to resistance to adopting AI solutions.
My view is that if 80 percent of our work is data preparation, then ensuring data quality is the important work of a machine learning team.
Andrew Ng
Professor of AI at Standford University and founder of DeepLearning.AI
March 2021 https://www.deeplearning.ai/the-batch/issue-84/
Insights on Effective AI Integration by High Performers
- Strategic Alignment: High-performing companies often succeed in AI adoption by aligning AI initiatives with their overall business strategy. They ensure that AI projects are not just technical exercises but are closely tied to key business objectives.
- Investment in Talent and Training: These organizations invest heavily in training their workforce in AI literacy and hire specialists who can bridge the gap between AI technology and business applications.
- Fostering an AI-Positive Culture: High performers work towards creating a culture that embraces AI. This includes leadership support for AI initiatives, encouraging a mindset of innovation and continuous learning, and addressing fears and misconceptions about AI among employees.
- Ethical AI Use and Governance: Effective AI integration also involves establishing clear guidelines and governance structures around AI use, focusing on ethical considerations, data privacy, and compliance with regulatory standards.
The journey towards AI adoption and achieving organizational readiness for AI integration is multifaceted. It requires not only technological investment but also strategic planning, cultural shifts, and a focus on ethical and responsible AI use. High-performing companies set themselves apart by addressing these aspects holistically, ensuring that their AI initiatives drive substantial business value and innovation.
Looking Ahead to AI in the Future
As we venture further into the era of AI and generative AI (Gen AI), understanding future trends and preparing for the next wave of AI innovation becomes crucial for CEOs and business leaders. This section delves into the anticipated developments in AI, strategies for staying ahead in the AI curve, and key recommendations for CEOs to strategically position their organizations for the unfolding AI revolution